In modern dentistry, we take x-rays fairly frequently. The average patient will receive four "periodic" radiographs annually, and an entire "full mouth" set of images every five to seven years (depending on multiple factors). Why do we need so many pictures? As it turns out, x-rays are an invaluable tool in diagnosing, documenting and monitoring changes in dental diseases. Take a look!
Dental x-rays give a dentist much more information that simply "looking in the mouth." In regards to tooth decay, radiographs can show cavities forming in areas that are impossible to visualize, such as in-between two teeth. Furthermore, they give more information on the location and depth of decay, helping inform decisions on placing fillings versus crowns, the risk of nerve irritation and what materials to use to fill the tooth. In most instances, we will not perform a filling on a tooth without an acceptable x-ray of the effected area. Radiographs are also necessary in assessing gum disease and bone loss. They can document the amount and pattern of recession, helping make decisions on dental cleanings and possible periodontal surgeries. In severe circumstances, heavy tartar hidden beneath the gum line will be visible on radiographs as well.
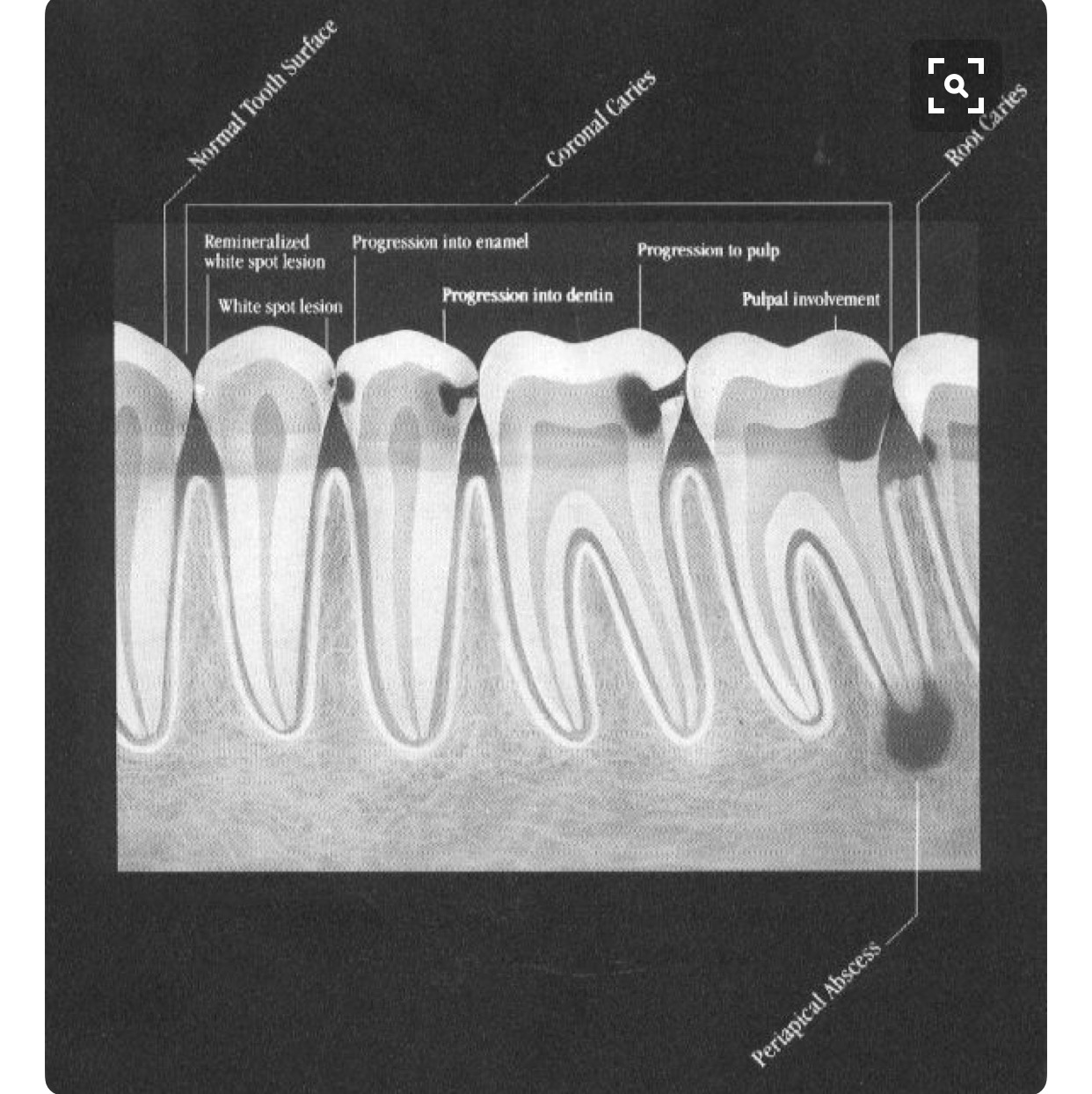
This image shows the progression of cavities, as seen on dental x-rays. In the last image, the decay has reached the tooth's nerve, necessitating a root canal
X-rays are also of great use in documenting and monitoring dental problems. Particularly in working with insurance companies, radiographs help demonstrate the necessity of certain procedures. This can improve the approval process and speed up reimbursements. Additionally, x-rays can help track the changes in dental conditions over time, aiding in decisions on treatment or continued monitoring.
This image shows the progression of gum disease, as seen on an x-ray. The small white bumps that form on the sides of the teeth are tartar below the gumline.
Radiographs are useful in visualizing much more than gum disease and tooth decay. Procedures like root canals, extractions and implants are impossible to perform without good radiographs. To learn more about the diagnostic tools we use in dentistry, please give our office a call.