Before explaining how a root canal works, it is important to understand the different parts of the tooth and what they do. There are three basic layers to all teeth- the enamel, the dentin and the nerve/pulp. The enamel is mostly inorganic (nonliving) material and gives the tooth its strength and rigidity (it’s the hardest material in the human body!). Dentin provides support to the enamel and contains a mix of living and nonliving materials. The innermost layer is the pulp chamber and nerve canal. This space contains innervation that provides information on biting pressure, temperature and pain to the central nervous system. It is mostly organic material and has has it’s own blood supply.
Different teeth will have different numbers of canals. The number varies between tooth types, arch location and even person to person. In general, teeth typically have between one and four canals, with posterior teeth having more than anteriors. On top of this, a tooth can have any number of accessory canals.These can range in size from easily visible to microscopic.
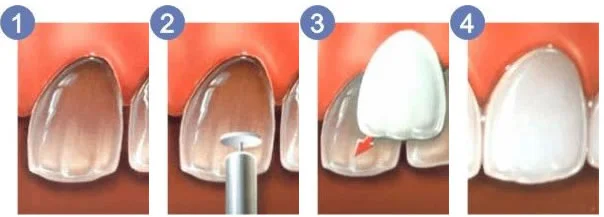
With this information in mind, let’s discuss root canals. In the most basic terms, a root canal is performed by removing the root/nerve from the tooth, cleaning out the now-empty space and filling it with a stable material. Why would we remove the nerve from a tooth? This is typically done because:
A) Long term decay, stress or fracture has aggravated the nerve and it is causing constant pain. This is what happening when patients come in with a “hot tooth.”
B) The aggravated nerve has now “died,” leaving a perfect alcove of organic material for bacteria to feed on. Here, patients might have very little feeling in the tooth and may notice a change in color to a grayish hue.
C) Bacteria have found the dead tissue and there is an active infection. The bacterial abscess can be seen on an X-Ray and the patient will feel soreness, swelling or even draining from the gum tissue.
Condition A will eventually progress to condition B and usually to condition C. Since active infections are both difficult to treat and potentially life threatening, we will usually treat dying nerves early-on and aggressively. Waiting can often lead to more pain and higher long term costs to our patients.
The actual root canal procedure is based on a simple ideology: If you remove the dying/dead nerve, you remove the source of pain and bacterial “food.” We start by getting you numb using standard dental anesthesia. You should not be able to feel any part of this procedure, from start to finish. The tooth is then isolated using a dental dam to keep your saliva and the inner tooth completely separated. We access the tooth canal and begin clean out the canal. We use a system of specialized files to shape and clean the canal, along with a number of sterilizing irrigants to eliminate any bacteria. Once the canal is the right size and shape (confirmed via X-Ray), we fill it with a material called gutta percha. Modern gutta percha is engineered in a lab, and is extremely resistant to deterioration, infection or absorption.